Starting with the impact of Health Information Technology on patient safety, this exploration offers a compelling and insightful look into the crucial role technology plays in healthcare today.
Subsequently, diving into the specifics of how HIT enhances patient safety measures and reduces medical errors.
Definition of Health Information Technology (HIT)
Health Information Technology (HIT) encompasses the use of technology to manage healthcare information, improve healthcare delivery, and ensure patient safety. It involves the electronic management of health information to support clinical decision-making, patient engagement, and overall healthcare operations.
Examples of HIT Tools in Healthcare Settings
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs): Digital versions of patients' paper charts, containing medical history, diagnoses, medications, treatment plans, immunization dates, allergies, radiology images, and lab test results.
- Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS): Software tools that provide healthcare professionals with knowledge and patient-specific information to enhance decision-making in patient care.
- Telemedicine: The use of technology to provide remote clinical services to patients, enabling healthcare professionals to evaluate, diagnose, and treat patients from a distance.
- Health Information Exchange (HIE): Platforms that allow healthcare providers to securely share patient information electronically, facilitating coordinated care and improving patient outcomes.
Significance of HIT in Modern Healthcare Systems
Health Information Technology plays a crucial role in modern healthcare systems by:
- Improving patient safety through accurate and timely access to patient information.
- Enhancing care coordination by enabling healthcare providers to share information seamlessly.
- Reducing medical errors through decision support tools that alert clinicians to potential issues.
- Increasing efficiency by streamlining administrative tasks and reducing paperwork.
- Empowering patients to actively participate in their healthcare decisions and manage their health information.
Importance of Patient Safety in Healthcare
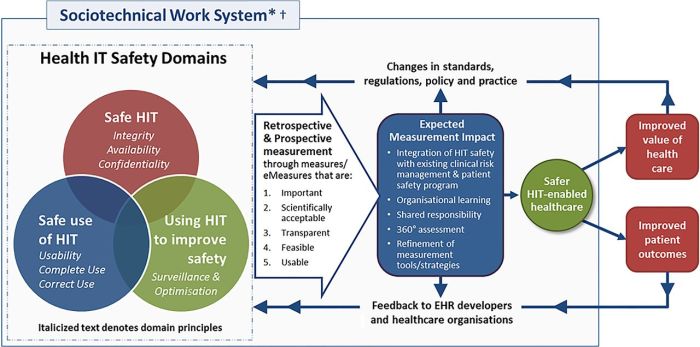
Patient safety is a critical aspect of healthcare that focuses on preventing harm to patients during the provision of medical services. Ensuring patient safety not only improves the quality of care but also enhances patient outcomes and overall healthcare system performance.
Common Risks to Patient Safety in Healthcare
In healthcare settings, various factors can pose risks to patient safety, leading to adverse events and medical errors. Some common risks include:
- Medication errors: Incorrect dosages, administration, or prescriptions can result in harmful effects on patients.
- Healthcare-associated infections: Infections acquired during hospitalization due to inadequate infection control practices can lead to complications.
- Communication breakdowns: Miscommunication among healthcare providers or with patients can result in misunderstandings and errors in treatment.
- Surgical errors: Mistakes during surgical procedures, such as wrong-site surgery or instrument retention, can have severe consequences for patients.
Impact of Errors on Patient Outcomes
Errors in healthcare can have detrimental effects on patient outcomes, ranging from minor harm to severe complications, and even death. Some of the impacts of errors on patient outcomes include:
- Increased hospital stays and healthcare costs
- Prolonged recovery periods and potential long-term disabilities
- Loss of trust in healthcare providers and the healthcare system
- Patient dissatisfaction and emotional distress
Role of Health Information Technology in Improving Patient Safety
Health Information Technology (HIT) plays a crucial role in enhancing patient safety measures within healthcare settings. By leveraging technology to streamline processes and improve communication, HIT can significantly reduce medical errors and improve overall patient outcomes.
Enhancing Patient Safety Measures
- HIT systems allow for easy access to patient information, ensuring healthcare providers have up-to-date and accurate data at their fingertips.
- Electronic health records (EHRs) enable quick retrieval of patient history, medications, allergies, and other critical information, reducing the risk of medication errors and adverse reactions.
Comparison with Traditional Record-Keeping
- Unlike traditional paper-based record-keeping, HIT systems offer real-time updates and alerts, prompting healthcare providers to take necessary actions promptly.
- Electronic systems also facilitate seamless communication between different healthcare providers, ensuring continuity of care and reducing the chances of miscommunication.
Examples of How HIT Reduces Medical Errors
- Decision support tools embedded in HIT systems can flag potential drug interactions, allergies, or dosage errors, alerting healthcare providers before administering treatment.
- Barcoding systems linked to EHRs help verify patient identities and medication accuracy, minimizing the risk of administering the wrong medication or dosage.
Implementation of Health Information Technology for Patient Safety
Implementing Health Information Technology (HIT) in healthcare settings is crucial for enhancing patient safety through improved data management and communication. Below are the steps involved in implementing HIT for improved patient safety:
Steps in Implementing HIT for Patient Safety:
- Assessing Current Systems: Evaluate existing systems and identify areas where HIT can be integrated to enhance patient safety.
- Setting Clear Objectives: Define specific goals for implementing HIT, such as reducing medication errors or improving care coordination.
- Choosing the Right Technology: Select HIT solutions that align with the organization's needs and budget constraints.
- Training Staff: Provide comprehensive training to healthcare professionals on how to effectively use the new HIT systems.
- Testing and Optimization: Conduct thorough testing of the HIT systems to ensure they function properly and make necessary adjustments for optimal performance.
Challenges in Adopting HIT for Patient Safety:
- Financial Constraints: Healthcare organizations may face budget limitations when investing in HIT implementation.
- Resistance to Change: Staff members may resist transitioning to new technologies, impacting the adoption process.
- Data Security Concerns: Ensuring patient data privacy and security while using HIT systems is a significant challenge for healthcare facilities.
Success Stories of Healthcare Facilities with HIT Integration:
- Johns Hopkins Hospital: Implemented a comprehensive HIT system that reduced medication errors by 50% and improved patient outcomes.
- Mayo Clinic: Successfully integrated HIT to enhance care coordination and streamline communication among healthcare teams, leading to better patient safety measures.
Data Security and Privacy Concerns in Health Information Technology
Data security and privacy are paramount in Health Information Technology (HIT) systems to protect sensitive patient information from unauthorized access or breaches. Ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of patient data is crucial for maintaining trust in healthcare organizations and safeguarding patient safety.
Importance of Data Security and Privacy in HIT Systems
- Unauthorized Access: Electronic storage of patient information increases the risk of unauthorized access by hackers or malicious insiders.
- Data Breaches: Breaches in HIT systems can lead to exposure of personal health information, resulting in identity theft or fraud.
- Legal Compliance: Healthcare organizations must comply with regulations such as HIPAA to protect patient privacy and avoid legal repercussions.
Potential Risks Associated with Storing Patient Information Electronically
- Identity Theft: Patient data stored electronically can be vulnerable to identity theft if security measures are not robust.
- Data Loss: Technical failures or system crashes can result in the loss of patient information, impacting patient care and safety.
- Ransomware Attacks: Healthcare organizations are at risk of ransomware attacks where hackers encrypt patient data and demand payment for its release.
Strategies to Mitigate Risks and Ensure Patient Data Confidentiality
- Encryption: Implementing encryption techniques can secure patient data during storage and transmission.
- Access Controls: Setting up access controls and user authentication mechanisms can limit unauthorized access to patient information.
- Regular Audits: Conducting regular security audits and risk assessments can identify vulnerabilities and address them proactively.
Summary
In conclusion, the integration of Health Information Technology in healthcare not only improves patient safety but also revolutionizes the way healthcare providers deliver quality care.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some common risks associated with HIT in healthcare?
Common risks include data breaches, system failures, and unauthorized access to patient information. Implementing robust security measures is essential to mitigate these risks.
How does HIT improve patient safety outcomes?
HIT improves patient safety by streamlining communication, reducing errors in diagnosis and treatment, and providing quick access to critical patient information.
What challenges do healthcare organizations face when implementing HIT for patient safety?
Challenges may include resistance from staff, financial constraints, and the need for extensive training. Overcoming these obstacles requires strong leadership and a comprehensive implementation strategy.